In our attempt to make this world free from cyber criminals, we have brought out different articles about hacking tools and apps. The attempt of putting such articles in public domain is to educate readers about the clear and present dangers about surfing online without taking necessary precautions. They are also meant to educate wannabe hackers about new tools, apps and techniques.
In continuation to our above, goal we bring this article on phishing tools. Phishing is the attempt to acquire sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details (and sometimes, indirectly, money), often for malicious reasons, by masquerading as a trustworthy entity in an electronic communication.
So, if you are essentially looking for a free phishing simulator or tools for your company, you have only three options: (1) Simple tools that allows you to create a simple email message and send it to one or numerous recipients using a specified mail server, (2) Open-source phishing platforms, and (3) Demo versions of commercial products.
You can use this tools to test the cyber defences of your company, provide cyber security training to your employees and friends.
(1) SecurityIQ PhishSim
Developed by InfoSec Institute, one of the many first benefits of SecurityIQ PhishSim is that after filling out a short online form, you get access to all benefits of software-as-a-service (SaaS) without having to pay for anything. It has no installation, no scripts to modify, and no servers to configure. All you need to do is simply sign up for a free account and start phishing and educate yourself. But, there are limitations, which include limited number of learners, branding and other customization options. However, the important components, such as using multiple templates (with over 100 templates to select from) in one campaign, report delivery and exporting features, campaign scheduling options, and an interactive phishing awareness education module, are included in the free account that allows you to run numerous extremely effective phishing campaigns.
(2) Gophish
Gophish is a powerful, easy-to-use, open-source phishing toolkit meant to help pentesters and businesses conduct real-world phishing simulations. The installation process is as simple as downloading and extracting a ZIP folder, as it is supported by most operating systems. While the limited features are considerately applied, the interface is simple and intuitive. Users can be easily added either manually or via bulk CSV importing. Email templates are easy to create and modify, creating campaigns is a direct process, and reports are pleasing to look at and can be exported to CSV format with many levels of detail. However, the most important disadvantage is that there no campaign scheduling options and no awareness education components.
(3) LUCY
LUCY is a hassle-free download of the free (community) version of the platform. You can download LUCY as a Debian install script or a virtual appliance. All you need is your email address and name for the same. While the web interface is attractive and maybe a bit confusing, there are many other features to explore. Designed as a social engineering platform, LUCY goes beyond phishing. It has awareness element along with interactive modules and puzzles. However, the community version of LUCY has too many restrictions to be efficiently used in an enterprise environment. Some important features such as campaign scheduling options, exporting campaign stats, and performing file (attachment) attacks, are not available under community license.
(4) Simple Phishing Toolkit (sptoolkit)
Simple Phishing Toolkit is a super easy to install and use phishing framework built to help information security professionals find human vulnerabilities. It offers an opportunity to combine phishing tests with security awareness education, with a feature that (optionally) directs phished users to a landing page with an awareness education video. Additionally, there is a tracking feature for users who completed the training. Ironically, the sptoolkit project was abandoned back in 2013. While a new team is trying to infuse new life in it, the documentation currently is rare and distributed all over the internet, making it a difficult task to realistically apply in an enterprise environment.
(5) Phishing Frenzy
Designed as a penetration testing tool, this open-source Ruby on Rails application has many features that could make it an effective solution for internal phishing campaigns. Compared to other similar tools, one of the main advantages is that you can manage your phishing tests more effectively as you can include the scope of your engagement as well when you create a new phishing campaign. Another advantage of Phishing Frenzy is that it can generate statistics regarding the users in scope (i.e. how many clicked the link?) which is always essential for the clients who order this type of test and the penetration tester as this information can be included as well in the final report. The stats can be viewed and easily saved into a PDF or an XML file, which is perhaps the most important feature of Phishing Frenzy. However, Phishing Frenzy is a Linux-based application, whose installation should not to be handled by a beginner.
(6) King Phisher
King Phisher is an open source Phishing Campaign Toolkit from SecureState. It has several features, which includes the ability to run multiple campaigns concurrently, web cloning capabilities, geo location of phished users, etc. Templates for both messages and server pages are contained in a separate template repository. While the user interface is clean and simple, it’s installation and configuration is not that easy. King Phisher server is only supported on Linux, with additional installation and configuration steps needed based on flavor and existing configuration.
(7) SpeedPhish Framework (SPF)
Created by Adam Compton, this python tool has many features that let you to quickly configure and carry out effective phishing attacks, including data entry attack vector. A tech-savvy security professional will be able to run phishing campaigns against several targets and can have a lot of fun with SPF. However, it will still remain a pentesting tool having many outstanding features (such as email address gathering) that may be hardly have importance for someone who is carrying out internal phishing tests.
(8) Social-Engineer Toolkit (SET)
Created and written by the founder of TrustedSec, the Social-Engineer Toolkit (SET) is an open-source Python-driven tool aimed at penetration testing around Social-Engineering. It has no graphical user interface (GUI). SET is the standard for social-engineering penetration tests and supported heavily within the security community. For phishing, SET allows to send spear-phishing emails, running mass mailer campaigns along with some more advanced options, such as adding list of target emails from a file and flagging your message with high priority. While it is effective as a penetration testing tool, but it is very restricted as a phishing simulation solution and does not include any campaign management features or reporting.
(9) SpearPhisher BETA
Developed by TrustedSec, SpearPhisher is a tool that doesn’t try to cheat anyone other than its phishing targets. It says it correctly in the description: “A Simple Phishing Email Generation Tool.” With an emphasis on ‘simple.’ SpearPhisher is a Windows-based program with a direct GUI designed for non-technical users. It lets you to swiftly craft a phishing email with customized From Email, From Name, and Subject fields and includes a WYSIWYG HTML editor and an option to include one attachment. By adding email addresses to To, CC, and BCC fields, you can send the crafted email to many recipients. Since 2013, the program has been in Beta, and hence it is likely that there may not be any updates in the near future
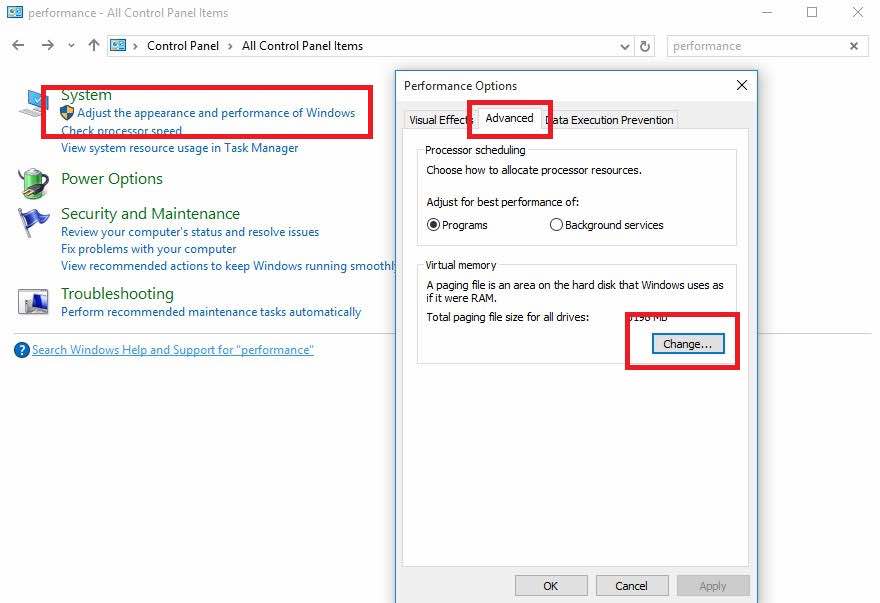
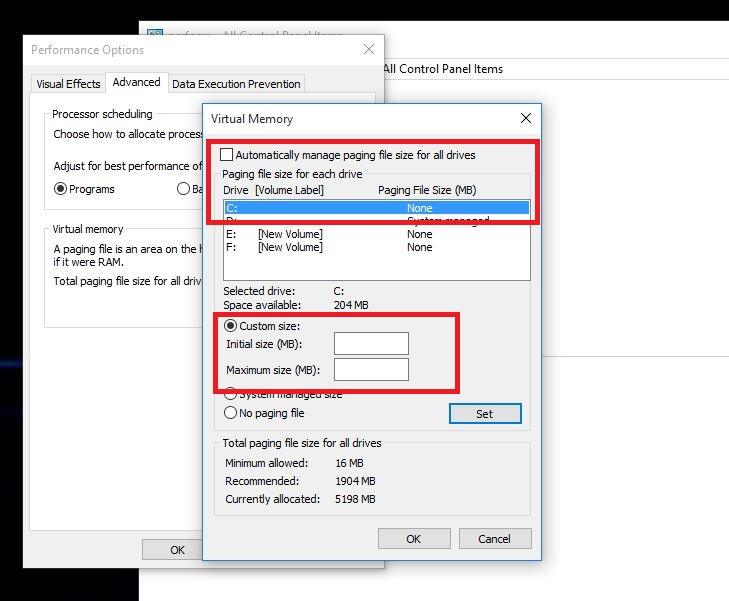
 Short Bytes: Many Windows users are facing Windows 10 slow performance issue in Windows 10. This appears in the form of input lags and could be fixed by tweaking some Page File settings in Windows 10. So, how to fix this slow performance issue in Windows 10 to boost system speed? Here is the answer.
Short Bytes: Many Windows users are facing Windows 10 slow performance issue in Windows 10. This appears in the form of input lags and could be fixed by tweaking some Page File settings in Windows 10. So, how to fix this slow performance issue in Windows 10 to boost system speed? Here is the answer.